ACDOCA table in SAP S/4HANA plays a critical role in the system’s architecture. As a finance professional or SAP user, understanding the ACDOCA table is essential to effectively manage financial transactions and reporting in the system. In this blog post, we will delve into the details of the ACDOCA table, its significance, structure, and how it functions within SAP S/4HANA.
What is ACDOCA Table in SAP?
The ACDOCA table in SAP S/4HANA is a Universal Journal Entry Line Items table that stores all financial data for an organization. It is a single table that consolidates data from various sub-ledger and other financial modules in the SAP system. The ACDOCA table replaced the traditional financial accounting (FI) and controlling (CO) tables in SAP ERP, making it a central repository for all financial transactions and reporting in SAP S/4HANA.
It plays a crucial role in simplifying financial processes and reporting in SAP S/4HANA. By consolidating all financial data in a single table, it eliminates the need for complex data reconciliation between FI and CO modules. This streamlined approach enables real-time reporting, improved data accuracy, and faster decision-making for finance professionals.
Key Features of ACDOCA Table
- ACDOCA is a centralized table the stores all transactional data that was previously stores in multiple tables in SAP ECC. This streamlines data access and provides a comprehensive view of all financial and management accounting data.
- ACDOCA integrates data from various modules such as Financial Accounting(FI). Controlling(CO), Material Ledger(ML) and Asset Accounting(AA), and the profitability Analysis(CO-PA). This allows a more holistic view of the financials.
- All transactions are posted in real time in the ACDOCA table. This ensures that the data is always up-to-date.
- ACDOCA table can store a large volume of the data with its more than 500 fields. This includes information about the General Ledger, Asset Accounting, Material Ledger, Controlling, and so on.
- ACDOCA table supports multi-dimensional reporting without the need for any aggregate tables.
- You can define up to 8 additional currencies beyond the 3 parallel currencies in FI and CO.
Structure of the ACDOCA Table
The ACDOCA table in SAP S/4HANA is structured to accommodate various types of financial transactions and data in SAP ERP. It consists of fields for document numbers, posting keys, amounts, currencies, and other relevant information for financial reporting. The table structure follows the universal journal concept, allowing for a flexible and comprehensive view of financial transactions.
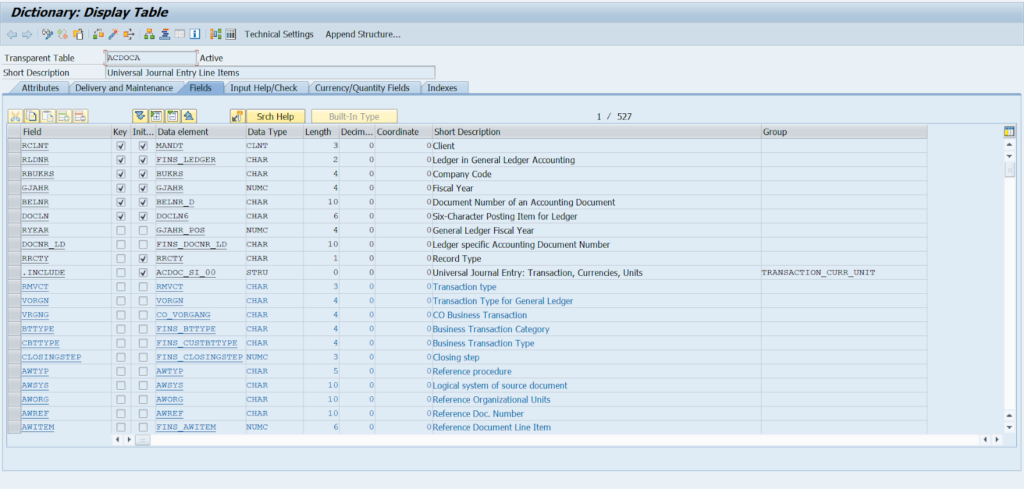
The primary key fields in the ACDOCA table include:
- RCLNT: Client
- RLDNR: Ledger in General Ledger Accounting
- RBUKRS: Company Code
- GJAHR: Fiscal Year
- BELNR: Document Number of an Accounting Document
- DOCLN: Six-Character Posting Item for Ledger
ACDOCA in SAP S/4HANA have more than 500 fields and number of standard ABAP CDS views available in to use in custom code. For more details information, please check ACDOCA technical details.
Custom Fields in ACDOCA table
To add additional custom fields in ACDOCA table in SAP S/4HANA, SAP recommends to use these extensibility options, which includes
- Classic Coding Block
- Classic CO-PA custom characteristics
- Key User Extensibility using following business context
- Coding Block
- Journal Entry Item
- Market Segment
For detailed information, please check ACDOCA Extensibility Options – A Master Guide
ACDOCA Migration
In order to utilize Finance in SAP S/4HANA, it is necessary to transfer existing user data from the General Ledger, Asset Accounting, Controlling, and Material Ledger. This data migration is essential as Finance in SAP S/4HANA relies on a consistent data model across all accounting areas.
The ACDOCA data table contains all line item documents and after the migration, all postings from the mentioned applications are stored in the ACDOCA table. Views with the same technical names are used to replace the following tables:
- General Ledger line item, totals tables, and application index tables (GLT0, BSIS, BSAS, FAGLFLEXA, FAGLFLEXT, FAGLBSIS, FAGLBSAS)
- Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable totals tables and application index tables (KNC1, KNC3, LFC1, LFC3, BSID, BSIK, BSAD, BSAK)
- Controlling line item and totals tables (COEP for certain value types, COSP, COSS)
- Material Ledger tables for parallel valuations (MLIT, MLPP, MLPPF, MLCR, MLCD, CKMI1, BSIM)
- Asset Accounting tables (ANEK, ANEP, ANEA, ANLP, ANLC)
By replacing these tables with views using the same names, all read accesses to the tables mentioned are preserved.










